acute glaucoma in babies
Angle-closure glaucoma may occur suddenly acute angle-closure glaucoma or gradually chronic angle-closure glaucoma. Ad Glaucoma comes with signficant warning symptoms.

Childhood Congenital Glaucoma Glaucoma Associates Of Texas
Infantile glaucoma develops between the ages of 1-24 months.

. Reveal why these glaucoma signs are so important to know right now. Glaucoma in children of all ages is rare unlike adult open angle chronic glaucoma which is relatively common. Ad Learn the early warning signs and symptoms of glaucoma right now.
Infantile glaucoma can cause complete blindness if left untreated. It occurs when the eye hasnt developed properly in the womb and this leads to issues with the flow of aqueous fluid out of the eye. However glaucoma can strike at any age and sometimes it affects children.
The following are the most common symptoms of childhood glaucoma. Glaucoma refers to a group of eye diseases in which fluid builds up in the eye creating pressure that damages the optic nerve and leads to vision loss. Glaucoma affects approximately 1 in 2000 children.
Glaucoma is rare in children as compared to the adult. Pediatric glaucoma is an eye disease that causes fluid to build up in the front part of a childs eye. Early-onset glaucoma is the term used when glaucoma appears in someone younger than 40.
Glaucoma in older children greater than 2 years old and adolescents is similar to glaucoma in adults. Developmental glaucoma is a type of glaucoma that occurs in babies young children and teenagers. Nearsightedness that gets worse.
3 The IOP usually ranges from 10 to 15 mm Hg in newborns whereas the IOP in children of school age resembles that of adults. Developmental glaucoma can be primary meaning it occurs on its own or. Redness in the sclera the white part of the eye sensitivity to light.
Without treatment glaucoma can cause permanent loss of eyesight. Older children and teens may have. One way to classify glaucoma is based on the age of onset.
Untreated glaucoma may lead to loss of side vision or permanent blindness. Babies with glaucoma may have. Glaucoma can affect one eye or both.
In babies doctors might notice eye shape or size issues that are clues a child might have glaucoma. Juvenile open-angle glaucoma which affects people between the ages. This obstruction increases the intraocular pressure which if untreated damages the optic nerve.
While glaucoma cant be cured early treatment can often control it. Primary infantile glaucoma is a rare developmental defect in the iridocorneal filtration angle of the anterior chamber that prevents aqueous fluid from properly draining from the eye. Childhood glaucoma is rare.
Primary congenital glaucoma PCG is a serious condition that needs attention. Signs of glaucoma in babies also include unusually large eyes or excessive tearing. Congenital glaucoma is present at birth.
If the fluid is unable to drain effectively it builds up inside the eye and causes the eye pressure to rise. Another way to classify glaucoma is to describe the structural abnormality or systemic condition which underlies the glaucoma. However when it does occur the symptoms may not be as obvious in children.
Most children with glaucoma will have an IOP that is higher than 22 mm Hg. The most common glaucoma in babies and small children. Can children get glaucoma.
It affects about one in every 10000 infants. Glaucoma in children older than two years is often secondary to other ocular disease or an underlying. It is characterized by a port-wine.
As the fluid continues to build the pressure increases in the childs eye and causes damage to the optic nerve. Developmental pediatric or childhood glaucoma usually refers to the latter developing after birth. Glaucoma can affect one eye or both.
Many children are diagnosed before they are 6 months old. When glaucoma occurs in children intraocular pressure inside the eye is too high due to a build-up of fluid. Older children and teens may have.
It may be present from birth or develop in the first few years of life. It affects children between birth and 3 years. However each child may experience symptoms differently.
A lot of blinking. Early-onset glaucoma arises because of an inborn abnormality of the structure andor function of the pressure drainage area in the eye the trabecular meshwork. A child can either be born with glaucoma or develop it later.
Glaucoma in children is rare and may affect about one in 5000 to 10000 children below two years of age. Depending on the severity of the abnormality it can be present when a baby is born or it can arise later. IOP in children of school age resembles that of adults.
Angle surgery is considered the mainstay of treatment for primary congenital glaucoma with a reported 70 to. Also called acute glaucoma or narrow-angle glaucoma this glaucoma type involves noticeable damage to the optic nerveIt is often a. In some cases a baby will be born with.
A dull or cloudy eye. Glaucoma is rare in children as compared to the adult. However each child may experience symptoms differently.
Excessive watering pain discomfort sensitivity to light loss of appetite are some symptoms. This damage can lead to peripheral side vision issues and blindness. Although infants and children under the age of 2 often present with signs and symptoms related to rapid ocular expansion under.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma can damage your vision cause severe eye pain nausea vomiting and headache. But in children glaucoma is characterized by IOP-related damage to the entire eye. Its possible for infants and children to have glaucoma.
Glaucoma with onset after age 3 years is called juvenile glaucoma. Alternatively it may be associated with either a systemic disorder such as Sturge-Weber syndrome or an ocular disorder such as aniridia or Peters anomaly. In some cases it also impairs breathing muscles forcing.
It is often used for. However when it does occur the symptoms may not be as obvious in children. Medical therapy in pediatric glaucoma is often supplementary to surgical management.
Most children with glaucoma will have an IOP that is higher than 22 mm Hg. Medical. A child can either be born with glaucoma or develop it later.
The following are the most common symptoms of childhood glaucoma. Other types of childhood glaucoma can occur at any time. Treatment may include medicines andor surgery.
7 hours agoThe condition called acute flaccid myelitis AFM attacks tissue in the spinal cord causing muscles and reflexes to weaken suddenly. While glaucoma is a concern of older people it can affect younger people too. Many children are diagnosed before they are 6 months old.
Like the most common form of glaucoma in adults primary open-angle glaucoma developmental glaucoma causes damage to the optic nerve due to higher-than-normal pressure inside the eye. Tears when not crying. Acute angle-closure glaucoma is a medical emergency.
It may be acquired eg as a result of trauma or uveitis. A corneal diameter of greater than 120 mm in any infant younger than 1 year is therefore suspicious for glaucoma. Signs and symptoms.
Most children with glaucoma will have an IOP that is higher than 22 mm Hg.
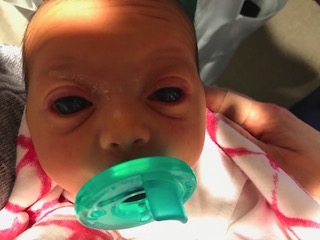
Severe Congenital Glaucoma In A Newborn Duke Health Referring Physicians

Leo 2 Weeks Post Surgery Boston Terrier Post Surgery Surgery
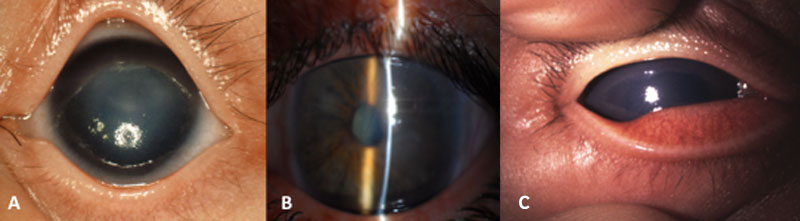
Glaucoma Information Congenital Glaucoma Glaucoma Information
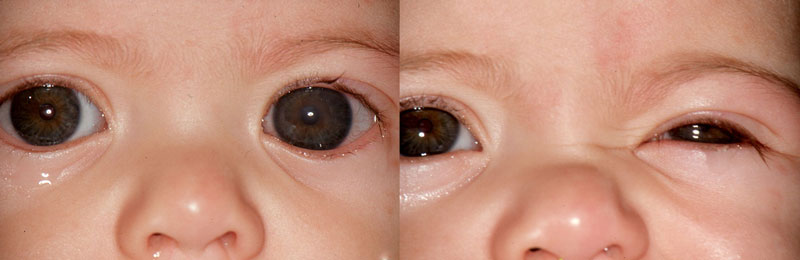
Glaucoma Information Congenital Glaucoma Glaucoma Information

Cyp1b1 And Myoc Variants In Neonatal Onset Versus Infantile Onset Primary Congenital Glaucoma British Journal Of Ophthalmology
Glaucoma Symptoms Treatment Prasad Netralaya
Pediatric Glaucoma Children S Eye Physicians

Childhood Congenital Glaucoma Glaucoma Associates Of Texas

Childhood Glaucoma Glaucoma Org
Congenital Glaucoma Europe American Academy Of Ophthalmology
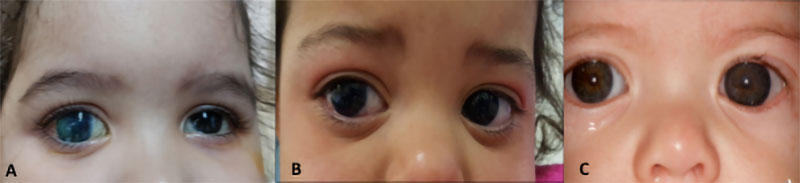
Glaucoma Information Congenital Glaucoma Glaucoma Information

Congenital Glaucoma An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Pin On Boston Terriers The More The Merrier

Rosh Review Itchy Eyes Allergy Eyes Itchy Eyes Remedy Allergies
Sturge Weber Syndrome And Secondary Glaucoma American Academy Of Ophthalmology



